Introduction to Oracle GoldenGate
Oracle GoldenGate enables the exchange and manipulation of data at the transaction level among multiple, heterogeneous platforms.
Oracle GoldenGate Architecture allows to replicate selected data, transactional changes, and changes to DDL.
It supports various business requirements like High Availability, Initial Load and Database Migration etc.
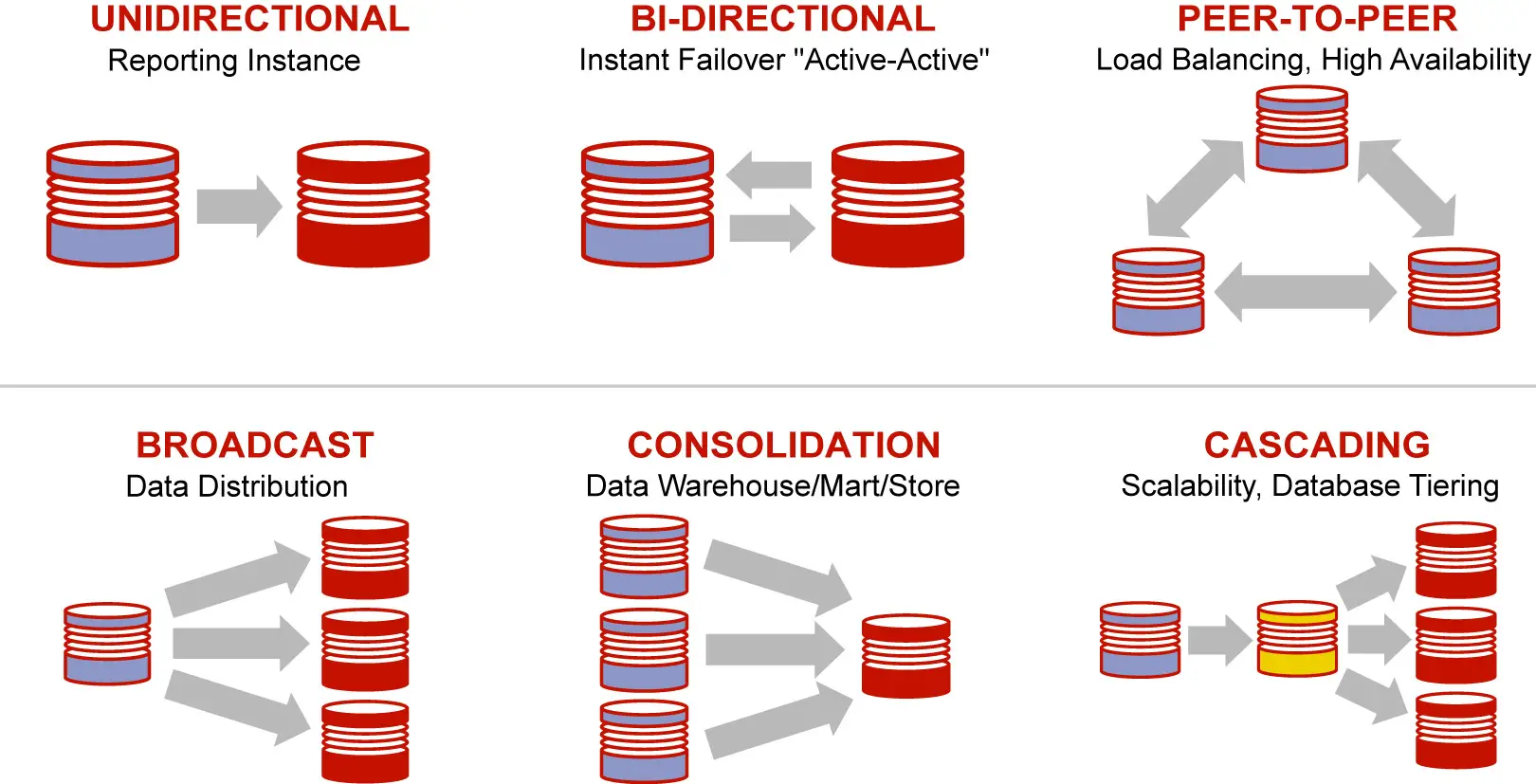
Oracle GoldenGate Supported Topologies
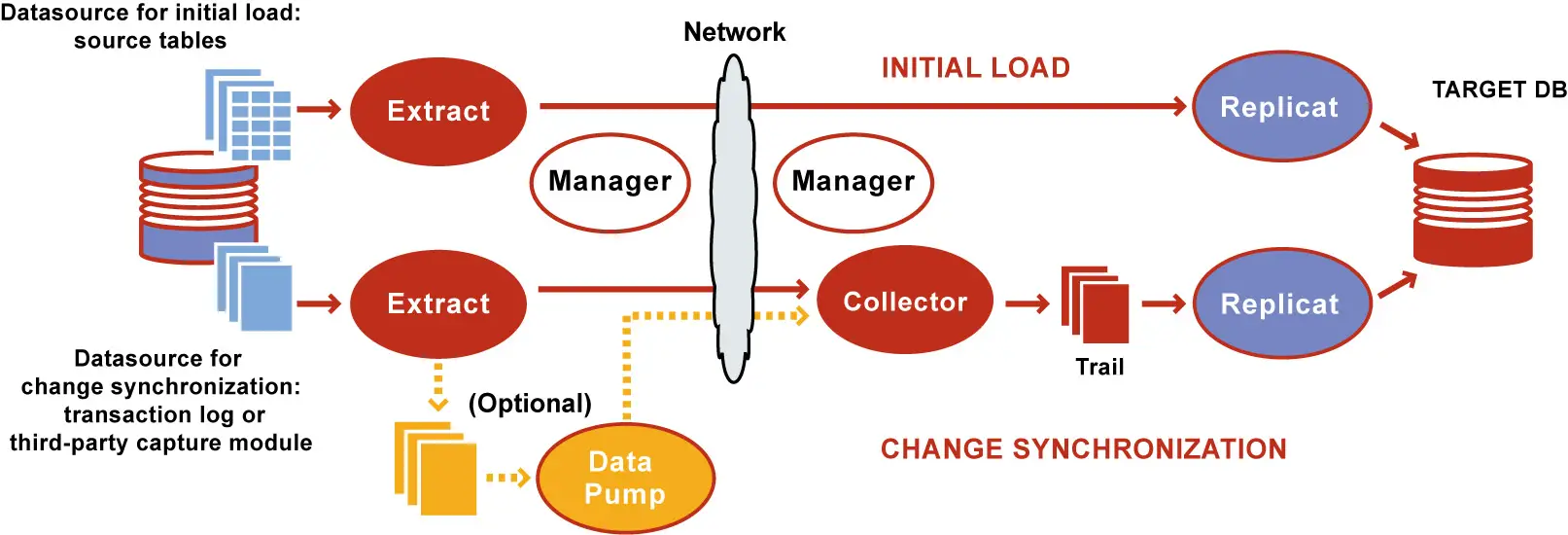
Oracle goldengate architecture
In simple terms, Extract process on source captures the transactions happening on source database and writes them to a trail file . The datapump process ships those trail files to the target host/db server with help of collector. Then the replicat process on target db server, reads those trail files and apply the transactions on target database.
Oracle GoldenGate is composed of the different components as mentioned below:
- Extract
- Data pump
- Replicat
- Trails or extract files
- Manager
- Collector
Extract: The Extract process is a capture mechanism of Oracle GoldenGate. Extract can be configured in the following ways
The Extract process is a capture mechanism of Oracle GoldenGate. Extract can be configured in the following ways
Initial load: Extract captures the data directly from their source objects.
Extract captures the data directly from their source objects.
Change Synchronization: Extract captures DML and DDL operations after the initial synchronization has taken place.
Extract captures DML and DDL operations after the initial synchronization has taken place.
The data source for the Extract process can be Source Tables (Initial Load), database recovery logs or transaction logs.
When configured for change synchronization, Extract captures the DML and DDL operations that are performed on objects in the Extract configuration. Extract stores these operations until it receives commit records or rollbacks for the transactions that contain them. When a rollback is received, Extract discards the operations for that transaction. When a commit is received, Extract persists the transaction to disk in a series of files called a trail, where it is queued for propagation to the target system. All of the operations in each transaction are written to the trail as a sequentially organized transaction unit. This design ensures both speed and data integrity.
Data Pump
It is secondary extract group in the GoldenGate configuration. With Data Pump configured the Primary Extract writes the captured information to a trail file on source system, Data Pump reads this trail and sends the information to remote trail file on the target over the network.
Reasons for using Data Pump:
- Protection against network and target failures
- You are implementing several phases of data filtering or transformation
- Consolidating data from many sources to a central target
- Synchronizing one source with multiple targets
Replicat
Replicat process on the target system reads the trail file and then reconstructs the DML and DDL operations and applies them to the database.
Trail Files
- Oracle GoldenGate stores the captured changes temporarily on the disk in a series of files called Trails.
- On Local system it is called as extract trail or local trail.
- On Remote system it is known as remote trail.
- Data Pump process reads the local trail on the source system and Replicat process reads the remote trail and applies the changes to the target database.
- Trail files are created using “ADD EXTTRAIL” and “ADD RMTTRAIL” command.
- Trail file name is created using two-characters appended with a unique 6 digit sequence number from 000000 to 999999. Example “/u02/ggs/dirdat/tr000001”
Manager
Manager is the control process of GoldenGate. This must be running before Extract or Replicat is started.
Manager Performs the below functions:
- Start Oracle GoldenGate processes
- Start dynamic processes
- Maintain port numbers for processes
- Perform trail management
- Create event, error, and threshold reports
Collector
Collector is a process that runs in the background on the target system when continuous, online change synchronization is active. Manager starts the Collector process automatically.
The collector does the following:
Upon a connection request from a remote Extract to Manager, scan and bind to an available port and then send the port number to Manager for assignment to the requesting Extract process.
Receives the captured changes sent by the Extract and writes them to the remote trail.
The collector can receive only from one Extract i.e. only one collector process for each Extract.
Overview of Process Types
Oracle GoldenGate can be configured with the following processing types:
- Online Extract and Replicat Process (Extract and Replicat DML and DDL during Change Synchronization)
- SOURCEISTABLE (initial load Extract)
- SPECIALRUN (Special Replicat run used during initial data loads on target system)
- Remote Task (Special type if initial load process in which Extract directly communicates with Replicat over TCP/IP)
Overview of groups:
Groups are defined to differentiate between multiple Extract or Replicat processes.
Group consists of process (Extract or Replicat), its parameter file, its checkpoint file and other files associated with it. For Replicat, a group may be associated with the checkpoint table.
Groups are defined using “ADD EXTARCT” and “ADD REPLICAT” commands in Oracle GGSCI.
SEE ALSO:
- Install Oracle Goldengate 12c On Linux 7
- Setting Up Table Replication In Oracle Goldengate
- Schema replication using oracle goldengate
- Adding New Table To A Existing Extract And Replicat In Goldengate
- Enable DDL replication using goldengate
- Disable DDL Replication In Goldengate
- Defgen Utility In Oracle Goldengate
- Obey Command In Goldengate
- COLS & COLSEXCEPT FILTER In Goldengate

Explanation is very clear,Expecting some more posts on golden gate topic.Thanks for sharing.
Dear Vijay,
We will try to post more useful posts on goldengate implementation.
Please share “enable DML replication in golden gate”